
STARS - Introduction
OPENING QUESTIONS: Scientists believe there are something like 100 - 200 billion stars in our own Milky Way galaxies.
Suggest a way that we might categorize stars to make it easier to study them
OBJECTIVE: I will be able to relate basic star formation after today's class.
I will also be able to list star categories after today's class.
WORD FOR TODAY:
- nebula ("a collection of dust and gas")
WORK O' THE DAY:
Viewing Schedule - Remember, if you'd like to apply to join our Observing Team, the very best thing you can do is to show up !
═══════════════════════════
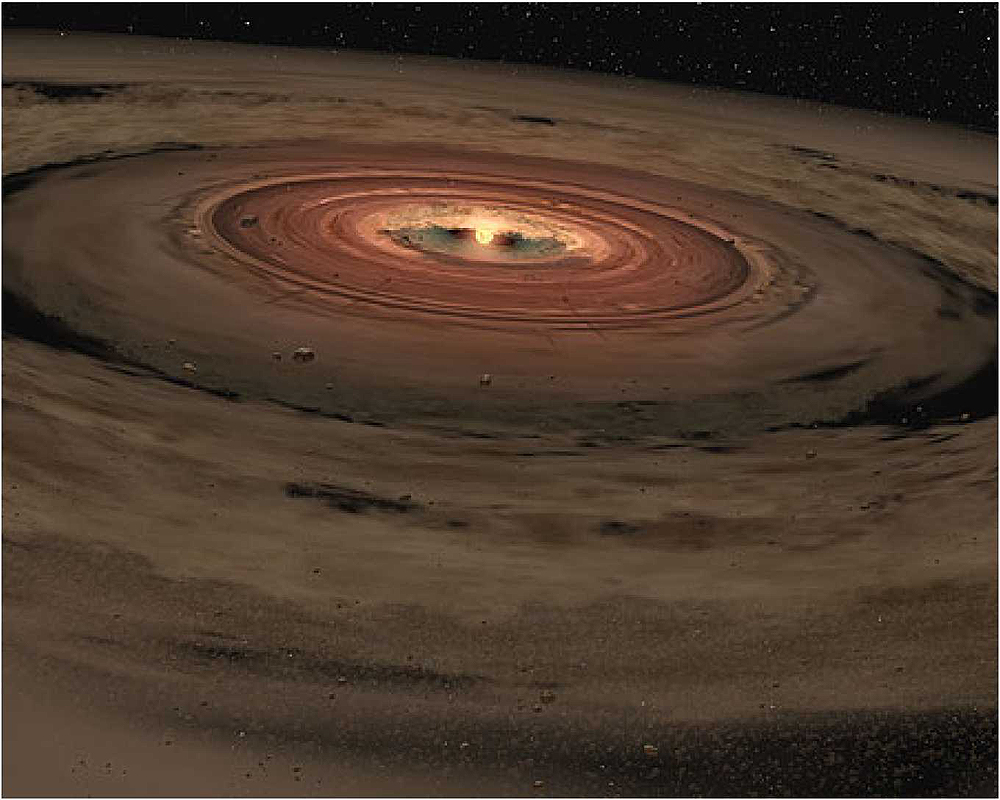
Let's revisit how our sun formed (since our sun IS a star this is a great recap for how stars are formed generally)
Nebulas are large clouds of dust and gas that are fairly common in our Milky Way galaxy.
- Imagine you are such a dust cloud--- minding your own business deep in the spaces between the stars.
- All at once a Super Nova happens.... which is to say a massive star blows up and sends a shockwave speeding through space.
- That shockwave gets all of your bits of dust and gas (remember, you're a nebula!) shimmying and shaking, dare I say, Rocking & A-Rolling?.
- As you start to move, the gravitational attractions of all your bits of dust and gas start pulling you into a cosmic whirlpool.
- As you move around and around collisions between the dust and gas occur.
- As those collisions occur, friction results.
- As friction results, temperatures rise.
- As temperatures rise, more energetic collisions occur.
- As more high energy collisions occur, temperatures rise.
- As temperatures rise, more collisions occur.
- As more collisions occur, the temperature rises.
- Eventually those temperatures get into the millions of degrees. And BOOM! the mashing of hydrogen and hydrogen atoms catches on in a continuous fusion reaction (making helium)
- VOILA! A Star is Born

═══════════════════════════
Our sun was formed this way about 4 billion years ago.
The outer bits of rock and gas continue to circle around, bashing into each other all the time.
The rocky bits condense into rocky planets or asteroids and in fact, our own Earth was formed this way about 4.5 billion years ago.
The other gaseous bits collapse into gaseous planets at the same time.
═══════════════════════════
Astronomers classify stars by color (really!)
Let's take a gander:
It also happens that these stars get smaller by color too! Blue super giants on the left side, red dwarfs on the right

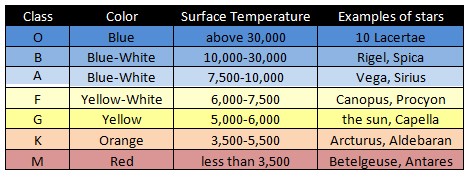
How do you remember that? With a mnemonic of course... spend a moment with your gcrew and work to come up with a mnemonic for that classification system.
Nothing?
How about:
Oh Be A Fine Goat, Kick Me!
As per usual, I REALLY don't want you to memorize specific values so let's do our goldilocks test:
O stars.... WAY WAY WAY TOO big and too hot and too bright
M stars.... WAY WAY WAY TOO small and too cool and too dim
G Stars... JUSSST RIGHT (like our SUN!)
Uh oh
Methinks it's time to shed our inhibitions and start to sing.... whatdya say?
YES!!! It's time for the SUN SONG!
But wait... I have my freshmen sing that and it has some inaccuracies... howzabout THIS version